Database
A database is an organized collection of data. It is the collection of schemas, tables, queries, reports, views, and other objects. The data are typically organized to model aspects of reality in a way that supports processes requiring information, such as modelling the availability of rooms in hotels in a way that supports finding a hotel with vacancies.
A database management system (DBMS) is a computer software application that interacts with the user, other applications, and the database itself to capture and analyze data. A general-purpose DBMS is designed to allow the definition, creation, querying, update, and administration of databases. Well-known DBMSs include MySQL, PostgreSQL, MongoDB, MariaDB, Microsoft SQL Server, Oracle, Sybase, SAP HANA, MemSQL and IBM DB2. A database is not generally portable across different DBMSs, but different DBMS can interoperate by using standards such as SQL and ODBC or JDBC to allow a single application to work with more than one DBMS. Database management systems are often classified according to the database model that they support; the most popular database systems since the 1980s have all supported the relational model as represented by the SQL language. Sometimes a DBMS is loosely referred to as a "database".
Database Model
A database model determines the information a database will contain and how it will be used and how the items in the database relate to one another.
Hierarchical Database
- Fields or records are arranged in related groups resembling a family tree
- Oldest and simplest; used in mainframes in 1970s
- Is rigid in structure and difficult to update
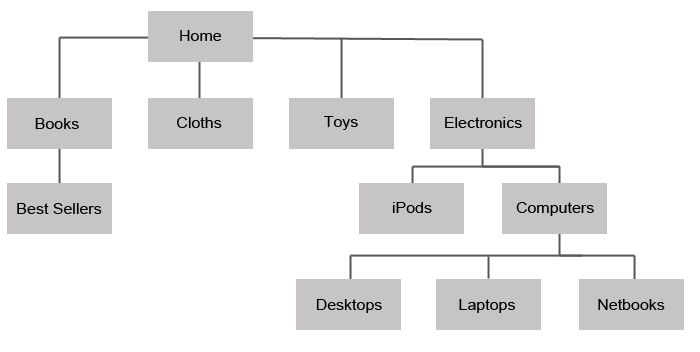
Network Database
- Fields or records are arranged in related groups resembling a family tree
- Oldest and simplest; used in mainframes in 1970s
- Is rigid in structure and difficult to update
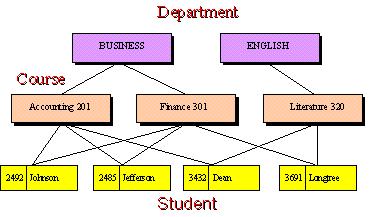
Relational Database
- grew out of the hierarchical and network database models
- Relates or connects data in different files through the use of primary keys, or common data elements
- Data stored in tables (relations, or files) of rows (tuples, or records) and columns (attributes, or fields)
- More flexible than previous models; built with SQL
- Users don’t need to know data structure to use the database

Test Yourself!
Take the quiz to see what you've learn
1. What is the database?
2. How many type of database?
3. Which one is not the type of database?
4. Why relational database is better than other type of database?
5. What is the database management system?
Question 1: The correct answer is an organized collection of data.
Question 2: The correct answer is 3.
Question 3: The correct answer is Database Model.
Question 4: The correct answer is All of above.
Question 5: The correct answer is a computer software application that interacts with the user, other applications, and the database itself to capture and analyze data.
You answered them all right!